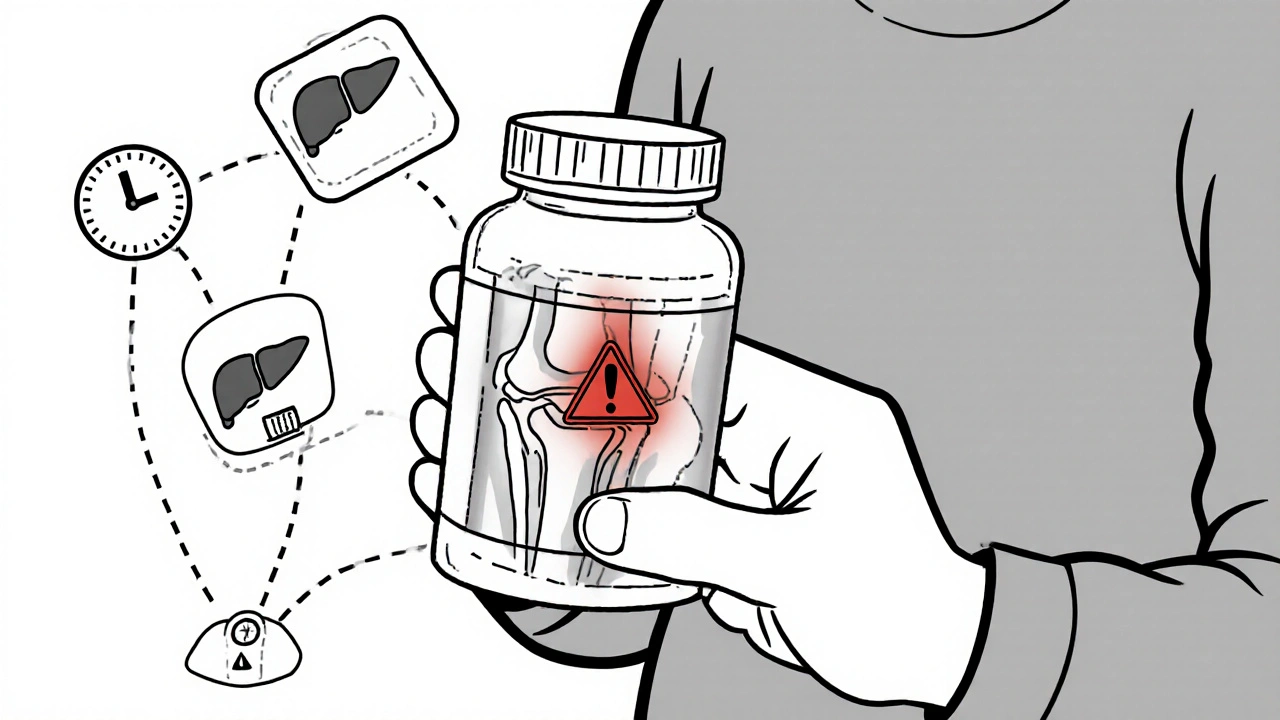
Acetaminophen is commonly used for joint pain, but new research suggests daily use may speed up cartilage loss in osteoarthritis. Discover safer alternatives and what the science really says.
Pain Relief: Effective Options for Joint, Muscle, and Chronic Pain
When you're dealing with pain relief, the process of reducing or managing physical discomfort caused by injury, inflammation, or chronic conditions. Also known as pain management, it's not just about popping a pill—it's about understanding what's causing the pain and how to stop it without side effects. Whether it's a stiff knee from osteoarthritis, a sore back from lifting, or nerve pain that won't quit, the right approach makes all the difference.
Not all pain relief is created equal. Diclofenac gel, a topical NSAID that targets inflammation right where it hurts works differently than oral pills. It delivers relief without flooding your stomach or kidneys. Then there's osteoporosis, a condition where bones weaken and often lead to chronic joint pain—but many people confuse it with osteoarthritis, which is cartilage wear, not bone loss. Diacerein, for example, slows cartilage damage in osteoarthritis but won't fix bone thinning. And if you're using pain meds for long-term relief, you need to know how excipients in generics might trigger reactions you didn't expect.
Topical options like capsaicin, lidocaine, and menthol creams are common, but they don't always work the same for everyone. Diclofenac gel has more clinical backing for joint pain than most OTC creams. Meanwhile, hip pain from labral tears or arthritis doesn’t mean you have to stop moving—modifying how you walk, sit, or lift can cut pain without surgery. Even simple things like hydration and posture matter when you're on blood pressure meds that cause dizziness. And if you're managing pain while also taking antidepressants or diabetes drugs, what you eat can change how well it all works.
You don't need to live with pain. The right solution depends on where it is, what's causing it, and how your body reacts. Some people find relief with gels, others need systemic meds, and some benefit from lifestyle tweaks alone. The posts below cover real cases, real comparisons, and real advice—from how to use CGM arrows to avoid blood sugar spikes that worsen nerve pain, to finding low-cost meds at community clinics if you're uninsured. You'll see what works for joint pain, what doesn't, and how to avoid traps like antibiotic shortages that make infections harder to treat. No fluff. No marketing. Just what you need to move better and feel less pain.
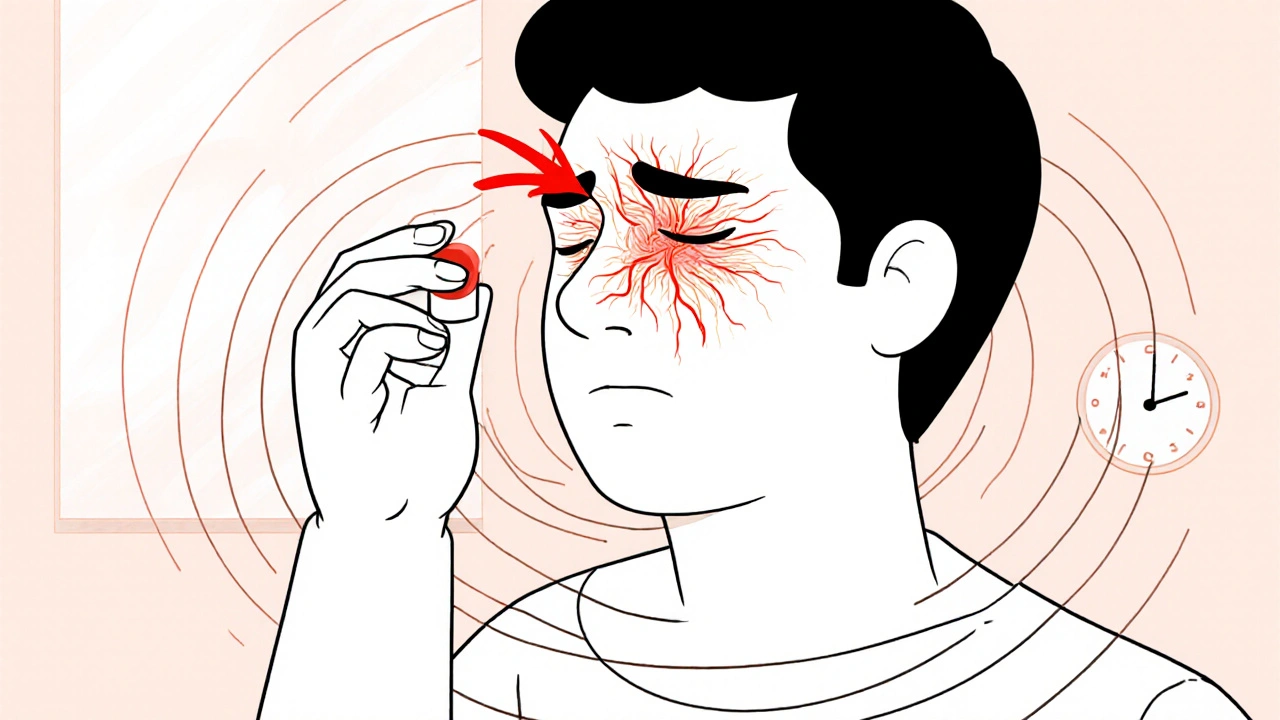
Ibuprofen is a fast-acting, effective treatment for common headaches like tension and mild migraines. Learn how it works, the right dosage, when to avoid it, and what to do if it doesn’t help.