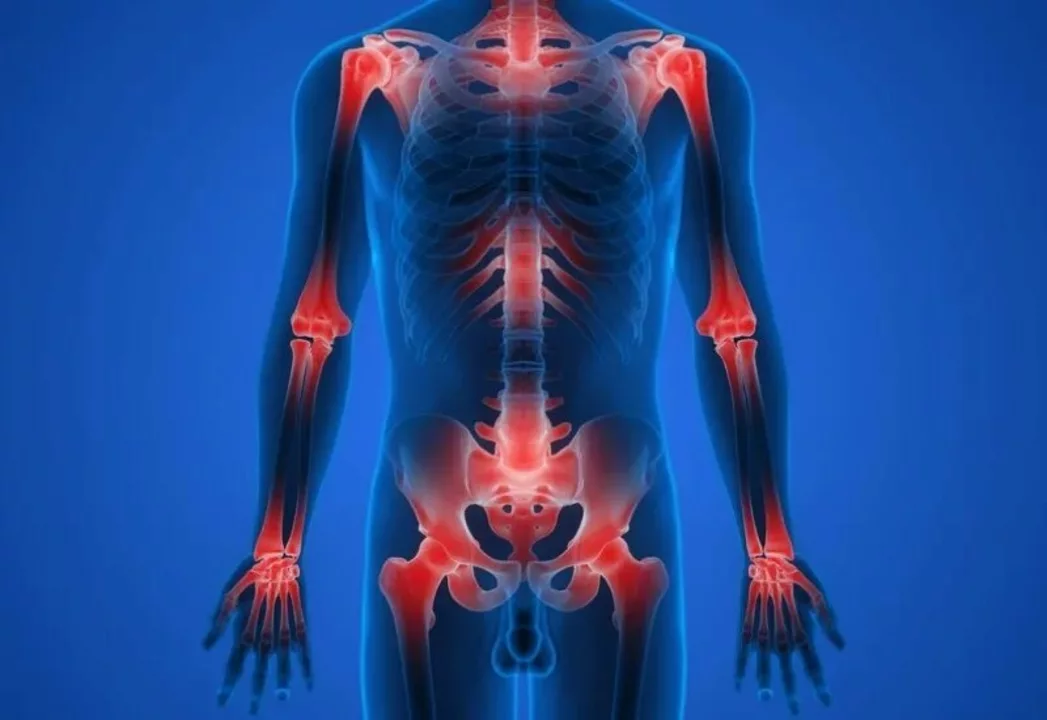
Understanding Joint Pain and Inflammation
Joint pain and inflammation are common symptoms that many of us experience, especially as we age. But what is the relationship between these two issues, and how does our immune system play a role in this process? In this article, we're going to explore the connection between joint pain, inflammation, and your immune system, and discuss how you can manage these symptoms for a healthier, more comfortable life.
What Causes Joint Pain and Inflammation?
Joint pain and inflammation can be caused by various factors, including injury, infection, autoimmune diseases, or simply wear and tear on the joints over time. Inflammation is a natural response of your immune system to protect your body from harm, but in some cases, this response can become chronic and lead to ongoing discomfort and pain.
When inflammation occurs, your immune system releases chemicals and cells that can cause swelling, redness, and warmth around the affected area. This response is intended to help your body heal, but in some cases, it can become excessive and lead to more harm than good. Understanding the role of inflammation in joint pain can help you take steps to manage your symptoms and improve your overall health.
The Immune System's Role in Joint Pain and Inflammation
Your immune system is responsible for protecting your body from foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. When your body detects a threat, your immune system responds by producing inflammation to help fight off the invader and promote healing. However, sometimes the immune system can become overactive and produce too much inflammation, leading to joint pain and other symptoms.
Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, are examples of conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and joint pain. In these cases, the immune system's response is not only excessive but also misdirected, resulting in damage to healthy tissues and ongoing pain and discomfort.
Recognizing the Signs of Inflammation
Recognizing the signs of inflammation is crucial for managing joint pain and understanding when to seek medical attention. Common signs of inflammation include swelling, redness, warmth, and sometimes stiffness around the affected joint. You may also experience pain or tenderness when touching the area or moving the joint.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Ignoring the signs of inflammation can lead to further damage and potentially more severe health issues down the line.
Managing Inflammation and Joint Pain
Fortunately, there are several ways to manage inflammation and joint pain, both through lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Some of the most effective strategies include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
- Taking over-the-counter or prescription anti-inflammatory medications
- Using hot and cold therapy to reduce swelling and alleviate pain
- Considering alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage
It's essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan to manage your joint pain and inflammation, as the appropriate treatment will depend on the underlying cause and severity of your symptoms.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods and Supplements
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and supplements into your diet can be an effective way to manage joint pain and inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, are known to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce joint pain. Additionally, fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can help combat inflammation and support overall health.
Some supplements, such as turmeric, ginger, and fish oil, have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may be beneficial for managing joint pain. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement to ensure it's appropriate for your individual needs and won't interact with any medications you're currently taking.
Physical Activity and Joint Health
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining healthy joints and reducing inflammation. Exercise helps to strengthen the muscles that support your joints, improve flexibility and range of motion, and promote better blood circulation, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
It's important to choose low-impact activities that won't place additional stress on your joints, such as swimming, cycling, or walking. If you're unsure where to start or have concerns about exercising with joint pain, consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist who can help you develop a safe and effective exercise routine.
Stress Management and Its Impact on Inflammation
Managing stress is another crucial aspect of reducing inflammation and joint pain. Chronic stress can lead to an overactive immune system and increased inflammation, so finding healthy ways to cope with stress is essential for overall well-being. Some effective stress management techniques include:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Deep breathing exercises
- Engaging in hobbies and activities you enjoy
- Spending time with friends and loved ones
- Seeking support from a therapist or counselor
By incorporating these stress-reducing practices into your daily routine, you can help keep inflammation in check and reduce your risk of developing chronic joint pain.
When to Seek Medical Help for Joint Pain and Inflammation
While some joint pain and inflammation can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments, it's essential to know when to seek medical help. If you're experiencing severe pain, swelling, or redness around a joint, have difficulty moving the joint, or notice any symptoms of infection (such as fever, chills, or warmth around the joint), it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional as soon as possible. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying issue that requires medical attention.
By understanding the role of inflammation and your immune system in joint pain, you can take proactive steps to manage your symptoms and improve your overall health. Remember always to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or treatment plan.






13 Comments